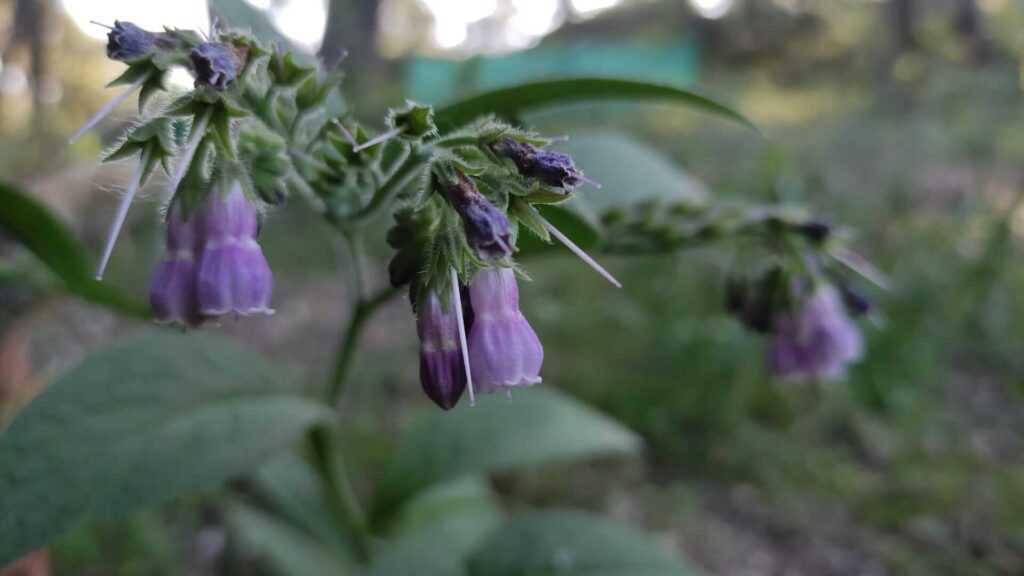
Russian Comfrey, scientifically known as Symphytum x Uplandicum, is an essential herbaceous plant for a vegetable garden. Its main property is that its root system is very deep, so it manages to bring up to the surface nutrients that are very difficult to obtain, mainly phosphorus.

Needs constant humidity, especially in summer
It prefers a semi-shaded place, ideally the shade of a tree.

Exhaust Hose / Dripper

Easy cultivation
Withstands intense frosts

By division of the root
Russian Comfrey Care
Soil Requirements
Russian Comfrey adapts to different types, but for it the ideal are fertile soils. If we have to take into account that since we want to get the nutrients stored in depth, the comfrey must be able to reach them, so it must be located in deep soil. Its roots can be up to 3 meters deep.
Soil Preparation
It does not need any special preparation. Obviously, comfrey should never be potted.
Light Requirements
It needs to be in a semi-shaded area, with a short period of sun exposure. It does not tolerate a long period of direct sun, especially during the hottest hours.
Irrigation
Comfrey requires regular watering, especially during dry periods. The soil should have constant moisture. It tolerates short periods of flooding well, its roots are resistant to wet rot.
Irrigation Methods
Drip irrigation or better yet, exudation hose irrigation, are the best options for Russian Comfrey.
Seedling Care
Pest Protection
Russian Comfrey is fairly resistant to pests and diseases, but can be susceptible to aphids and fungi such as powdery mildew and rust.
Comfrey in Winter
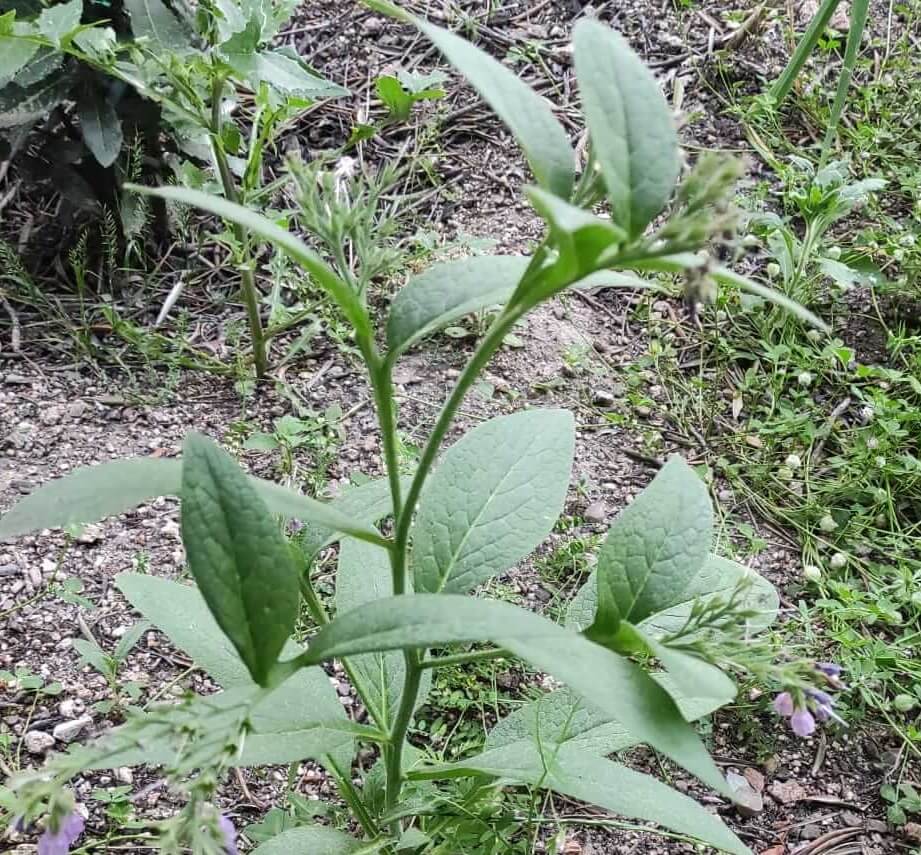

In areas where there are winter frosts, the plant will lose its leaves but will remain alive in its root system, resprouting in spring.
If frosts are very intense, and the area where it has been planted does not receive sun in winter, mulching can help. If it does receive sun, it is better not to mulch so that the rays warm the soil.
How to Reproduce Russian Comfrey
Reproduction by Division
Russian Comfrey is a hybridized plant, similar to what a mule would be in the animal world. It is a sterile plant, so its seeds are not fertile. Therefore we can only reproduce it by dividing its roots.
This process should be done in spring or autumn, taking into account that when dividing, each fragment must have roots and buds, minimum of 5 centimeters for the plant to thrive.
Uses of Russian Comfrey
Medicinal Uses
It has healing properties to heal wounds. It should be used with caution as it contains alkaloids that are toxic to the liver. We do not use it as a medicinal plant.
Uses for the orchard
This is certainly the use we will make of Russian Comfrey. As we have mentioned before, its deep root system is rich in nutrients that tend to go to the deep layers with irrigation or rain. Mainly we will be looking to obtain Phosphorus, one of the 3 NPK nutrients, and the most difficult to obtain by natural means. This is the reason why we will want to have Russian Comfrey.
Obtaining its nutrients
It is advisable to use the plant as little as possible in the first year so that it can develop, i.e., do not prune it too much.
The obtaining of its nutrients can be done in 3 ways, being complementary:
– By means of Comfrey slurry or tea.
– Directly mulching with its leaves in the bed (as long as they are free of diseases).
– Adding them to the compost. If we know or suspect that the plant has a disease, this will be the best method if we make hot compost.
Now that you are familiar with Russian comfrey, here are some recommendations that we think you may find useful:
🌿 Russian Comfrey Seeds
Grow this all-terrain plant and discover how to take advantage of its multiple uses.
👉 View on Amazon💧 Exhaling textile tape
Ideal for localized irrigation and water saving in orchards and gardens.
👉 View on Amazon


